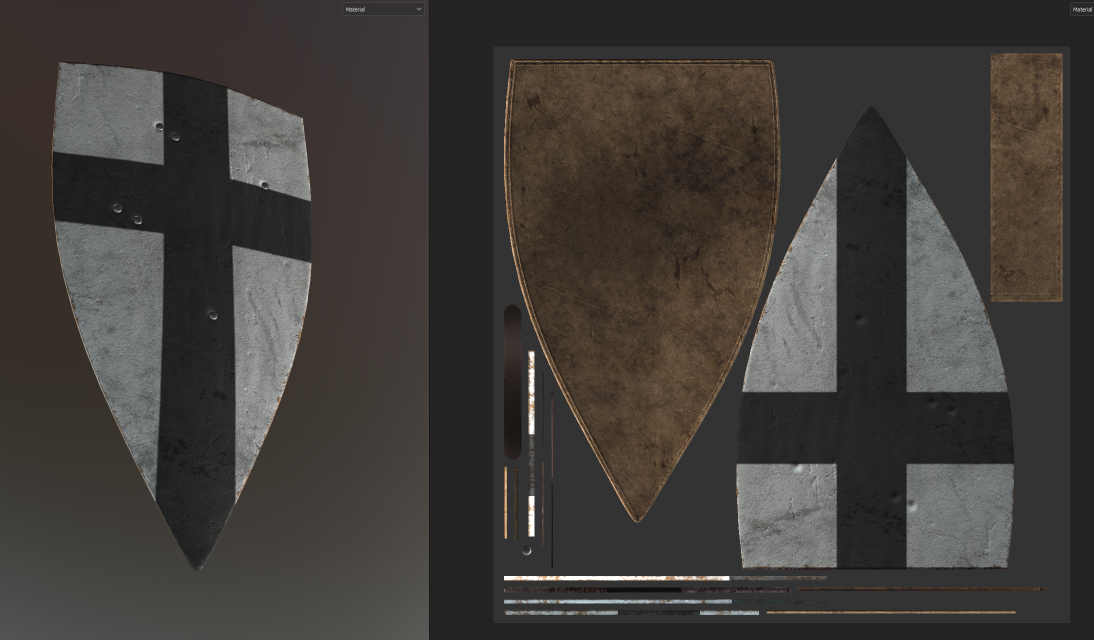
Terms
When I first started working with 3D in Bannerlord, I found it challenging to understand guides—both written and video—because I came from a coding background. Terms like meshes, UVs, and LODs were unfamiliar and felt meaningless to me. I spent time familiarizing myself with these concepts to gain a clear understanding, which greatly helped me progress.
To help others, I wrote this page to describe the most commonly used terms in 3D.
Model: A comprehensive 3D representation of an object that includes the mesh and additional data such as materials, textures, shaders, rigging, and animations.
Texture: An image applied to a model's surface to add color, detail, and realism.
Material: A set of properties that define how a model's surface interacts with light, including textures and shaders.
Weight Paint: A method of assigning influence to vertices for deformation, used in rigging to control how bones affect the mesh during animation.
Rigging: The process of adding a skeletal structure to a 3D model, allowing it to be animated by defining how it moves and deforms.
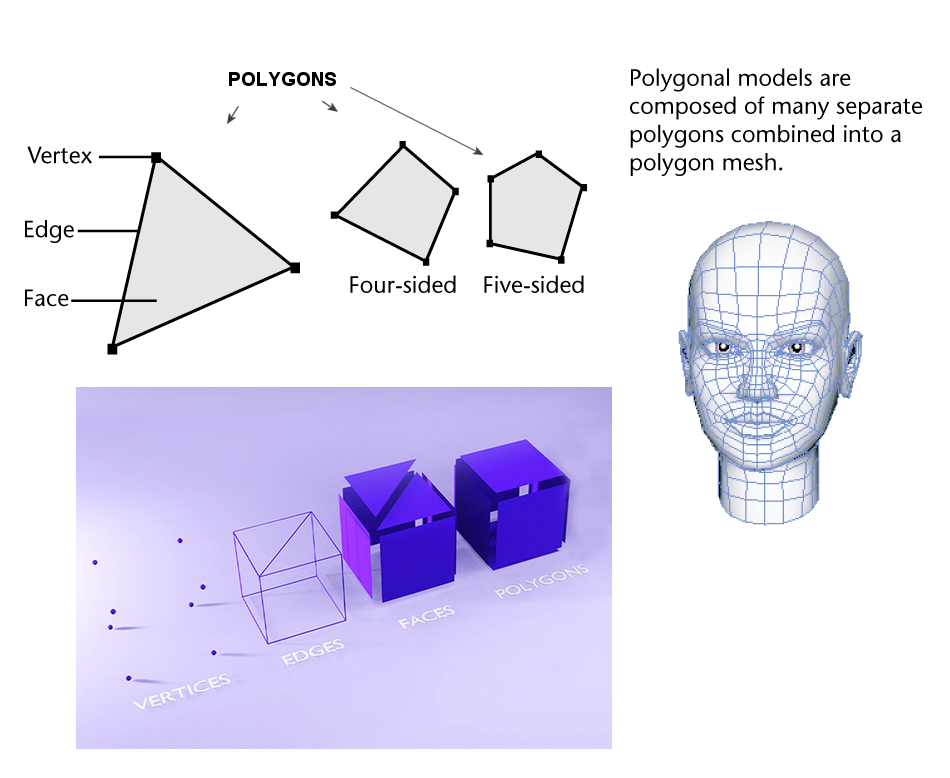
Mesh
Mesh: A collection of polygons (which are made of vertices, edges and faces) that defines the shape of a 3D object.
Vertex (plural: Vertices): A point in 3D space.
Edge: A straight line connecting two vertices.
Face: A flat surface enclosed by edges in a 3D model - the interior region of the polygon.
Polygon: A flat, two-dimensional shape formed by connecting three or more vertices with edges to create a closed figure, known as a face. Polygons are the basic units that make up the surfaces of a 3D model. The most common types are:
- Triangles: Polygons with three sides and three vertices. They are widely used because they are always planar and render efficiently.
- Quads: Polygons with four sides and four vertices. They are preferred in modeling workflows for ease of editing and smooth deformation during animation.
LOD
LOD (Level of Detail): A technique that adjusts the complexity of a 3D model based on its distance from the viewer to optimize performance. The further away the model is, the fewer parts are rendered.
UV Mapping
UV: A 2D coordinate system that allows to create 2D textures that are applied to the 3D object.